黄金分割法
1. プログラムの概要
goldsect - 黄金分割法で与えられた区間で関数の最小値を求める
2. C
/* * オリジナルの出典「C言語による最新アルゴリズム事典」奥村晴彦著 - P19 * インデントは変更してあります。 * 他にも、メッセージや変数名や処理を変更している場合があります。 */ #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> double goldsect(double a, double b, double tolerance, double (*f)(double x)) { double const r = 2.0 / (3 + sqrt(5)); /* 1 / φ^2 */ double c, d, fc, fd, t, u; /* make sure a < b */ if (a > b) { t = a; a = b; b = t; } u = r * (b - a); c = a + u; d = b - u; fc = f(c); fd = f(d); while (1) { if (fc > fd) { a = c; c = d; fc = fd; d = b - r * (b - a); if (d - c <= tolerance) { return c; } fd = f(d); } else { b = d; d = c; fd = fc; c = a + r * (b - a); if (d - c <= tolerance) { return d; } fc = f(c); } } } double f(double x) { return x * x; } int main() { double xmin = goldsect(-10, 10, 1e-6, f); printf("(x, y) = (%lf, %lf)\n", xmin, f(xmin)); /* expects (0, 0) */ xmin = goldsect(4, 20, 1e-6, f); printf("(x, y) = (%lf, %lf)\n", xmin, f(xmin)); /* expects (4, 16) */ }
イメージは次のようになります。
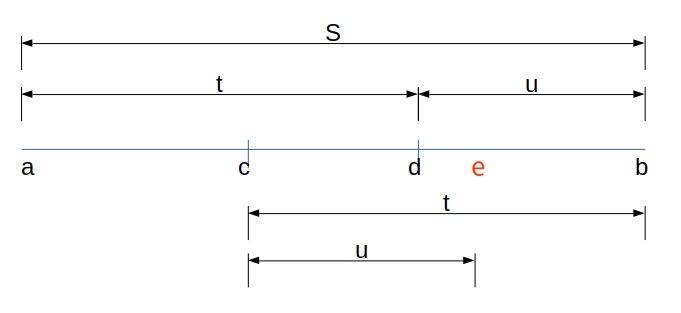
図1: 黄金比による分割
\(s : t = t : u\) になるような比率で、区間を分割しながらどんどん範囲を狭めていきます。
ここで \(u = s - t\) なので、上式に代入すると \(s : t = t : (s - t)\) となり、これを解いてみます。
\(s(s - t) = t^2\)
\(s^2 - st - t^2 = 0\)
\(\frac{s^2}{t^2} - \frac{s}{t} - 1 = 0\)
\(\frac{s}{t} = \frac{1 \pm \sqrt{5}}{2}\)
\(s > 0\) かつ \(t > 0\) なので
\(\frac{s}{t} = \frac{1 + \sqrt{5}}{2} = 1.618033988749...\)
この比率は黄金比と呼ばれ、記号 \(\phi\) で表わされることが多いです。
先のプログラムで double const r = 2.0 / (3 + sqrt(5)); としているところに黄金比が含まれています。
値が違っているのは、黄金比の逆数の二乗をとっているからです (\(\frac{1}{\phi^2}\))。
なぜそうなっているかというと、ちょっとややこしいです。
今、欲しいのはcとdのx値です。
そして \(c = a + u\) と \(d = b - u\) となっています。
ここで \(u\) を \(\phi\) で表わすことを考えてみます。
\(\frac{s}{t} = \phi\)
\(t = \frac{s}{\phi}\)
となります。
同様に、
\(\frac{t}{u} = \phi\)
\(u = \frac{t}{\phi}\)
となります。 そして、先の \(t = \frac{s}{\phi}\) を代入してやります。
\(u = \frac{s / \phi}{\phi} = \frac{s}{\phi^2}\)
となり \(s\) は \(a - b\) なので、
\(c = a + \frac{b - a}{\phi^2}\)
\(d = b - \frac{b - a}{\phi^2}\)
という結果を得ることができます。
3. Emacs Lisp
(defun goldsect (a b tolerance f) (let ((r (/ 2.0 (+ 3 (sqrt 5)))) c d fc fd temp u) ;; make sure a < b (when (> a b) (setq temp a a b b temp)) (setq u (* r (- b a)) c (+ a u) d (- b u) fc (funcall f c) fd (funcall f d)) (while (> (- d c) tolerance) (cond ((> fc fd) (setq a c c d fc fd d (- b (* r (- b a))) fd (funcall f d)) ) (t (setq b d d c fd fc c (+ a (* r (- b a))) fc (funcall f c))))) c)) (defun foo (x) (+ (* x x) 30)) (let ((xmin (goldsect -10 10 1e-10 'foo))) (message "(%f, %f)" xmin (foo xmin))) ;expects (0, 30)
4. Bash
#!/bin/bash function fmath { echo "scale=10; $@" | bc } function goldsect { a=$1 b=$2 tolerance=$3 f=$4 # make sure a < b if [ $a -gt $b ] then t=$a a=$b b=$t fi r=$(fmath "2.0 / (3 + sqrt(5))") u=$(fmath "$r * ($b - $a)") c=$(fmath $a + $u) d=$(fmath $b - $u) fc=$($f $c) fd=$($f $d) while true do if [ $(fmath "$fc > $fd") -eq 1 ] then a=$c c=$d fc=$fd d=$(fmath "$b - $r * ($b - $a)") if [ $(fmath "$d - $c <= $tolerance") -eq 1 ] then echo $c return 0 fi fd=$($f $d) else b=$d d=$c fd=$fc c=$(fmath "$a + $r * ($b - $a)") if [ $(fmath "$d - $c <= $tolerance") -eq 1 ] then echo $d return 0 fi fc=$($f $c) fi done } function foo { echo "$1 * $1" | bc } xmin=$(goldsect -10 10 0.0000001 foo) echo $xmin $(foo $xmin)
5. Fish
#!/usr/bin/fish function fmath math -s15 "$argv" end function goldsect set a $argv[1] set b $argv[2] set tolerance $argv[3] set f $argv[4] # make sure a < b if test $a -gt $b set t $a set a $b set b $t end set r (fmath "2.0 / (3 + (sqrt 5))") set u (fmath "$r * ($b - $a)") set c (fmath $a + $u) set d (fmath $b - $u) set fc ($f $c) set fd ($f $d) while true if test $fc -gt $fd set a $c set c $d set fc $fd set d (fmath "$b - $r * ($b - $a)") if test (fmath "$d - $c") -le $tolerance echo $c return 0 end set fd ($f $d) else set b $d set d $c set fd $fc set c (fmath "$a + $r * ($b - $a)") if test (fmath "$d - $c") -le $tolerance echo $d return 0 end set fc ($f $c) end end end function foo echo (fmath "$argv[1] * $argv[1]") end set xmin (goldsect -10 10 0.0000001 foo) printf "(%f, %f)\n" $xmin (foo $xmin) # expects (0, 0) set xmin (goldsect -5 -10 0.0000001 foo) printf "(%f, %f)\n" $xmin (foo $xmin) # expects (-5, 25)